A next generation mAb
MARGENZA is the first and only FDA-approved, Fc-engineered, HER2-targeted mAb designed to improve immune engagement1,2
Mechanism of action
See how the engineered Fc region of MARGENZA works.
MARGENZA is a mAb made up of 2 functional regions.1,3
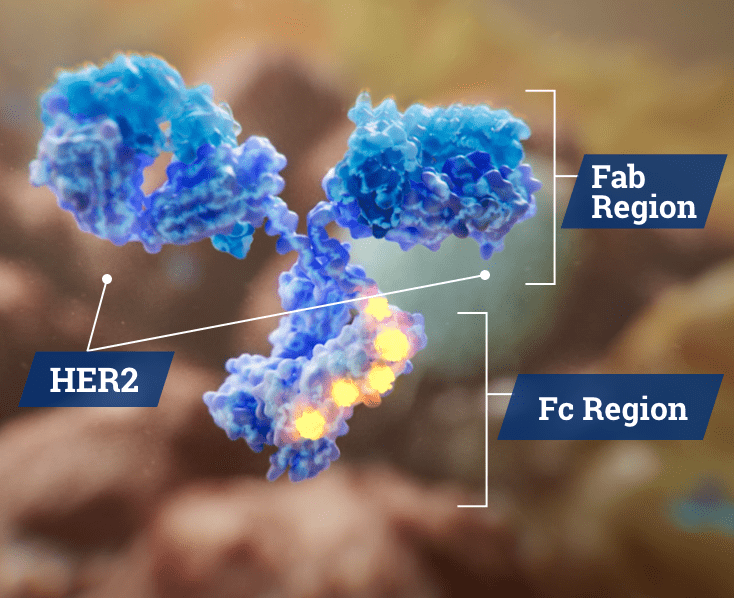
The anti-HER2 fragment antigen-binding (Fab) region of the antibody binds to the HER2 receptor on tumor cells. This interaction is the source of MARGENZA’s antiproliferative activity.1
The engineered fragment crystallizable (Fc) region of MARGENZA has been distinctly engineered in 5 locations.4 This mediates immune effects by recruiting the innate immune cells (natural killer [NK] cells and macrophages) in order to cause antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of the tumor cells.1,3
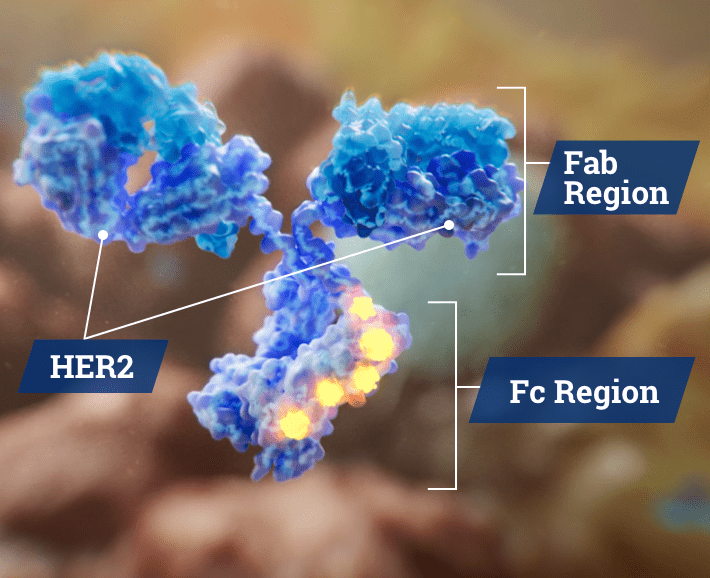
The anti-HER2 fragment antigen-binding (Fab) region of the antibody binds to the HER2 receptor on tumor cells. This interaction is the source of MARGENZA’s antiproliferative activity.1
The engineered fragment crystallizable (Fc) region of MARGENZA has been distinctly engineered in 5 locations.4 This mediates immune effects by recruiting the innate immune cells (natural killer [NK] cells and macrophages) in order to cause antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of the tumor cells.1,3
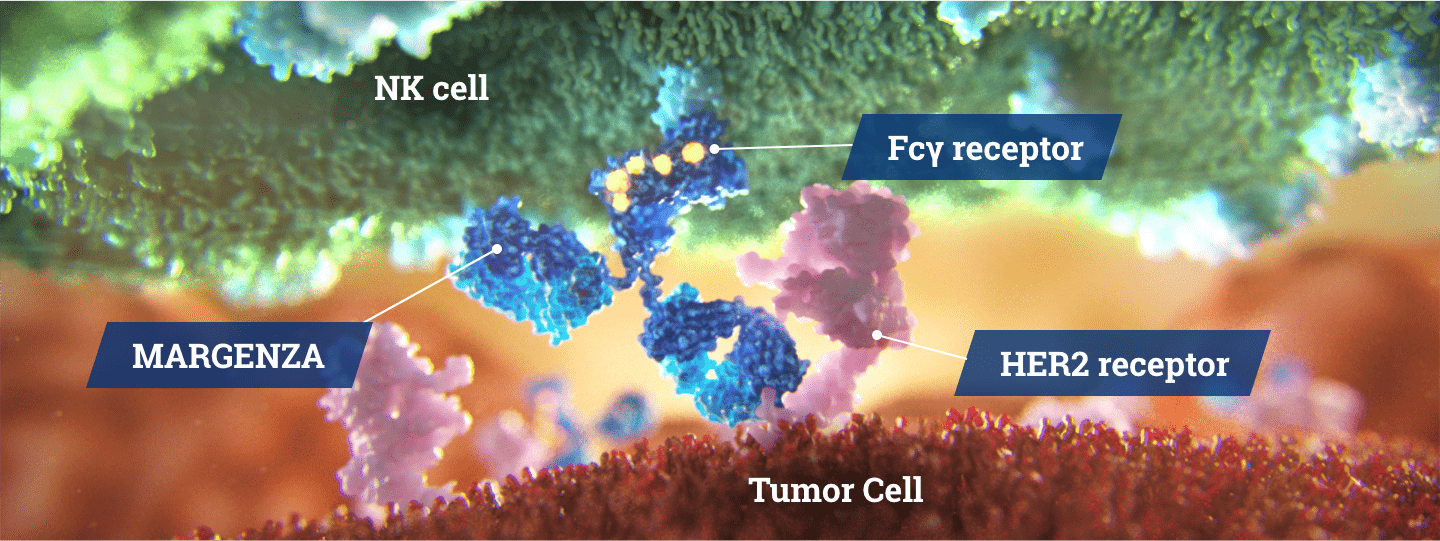
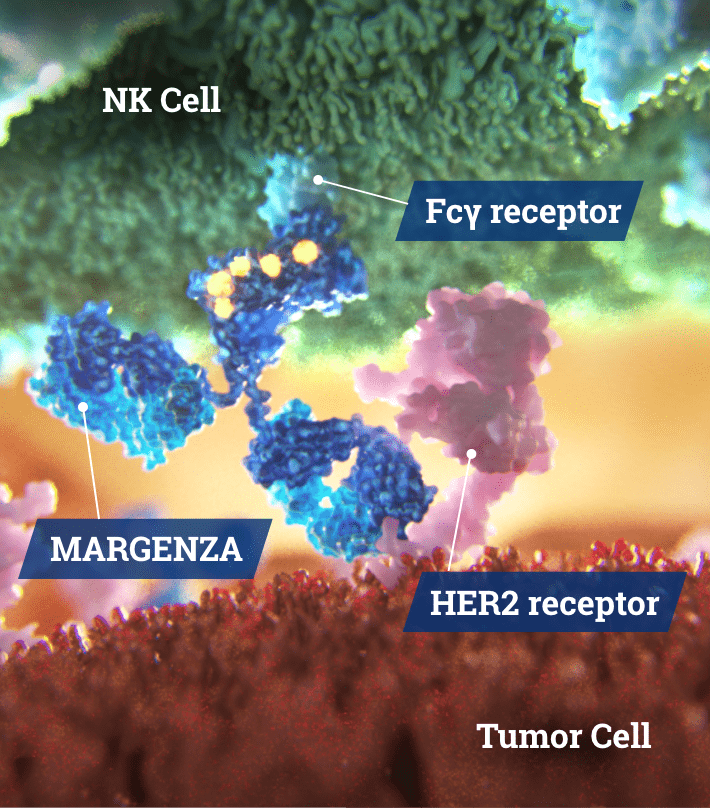
The engineered Fc region increases immune activity in vitro compared with trastuzumab1
The clinical relevance of in vitro data is unknown.
Direct Anti-Tumor Activity1
- Inhibits tumor cell proliferation
- Reduces shedding of HER2 extracellular domain
Fc Region Optimization1
- Increased binding to CD16A (activating)
- Decreased binding to CD32B (inhibitory)
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)1,3
- Immune cell-mediated anti-tumor activity
- Greater in vitro ADCC and NK cell activation
Direct Anti-Tumor Activity1
- Inhibits tumor cell proliferation
- Reduces shedding of HER2 extracellular domain
Fc Region Optimization1
- Increased binding to CD16A (activating)
- Decreased binding to CD32B (inhibitory)
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)1,3
- Immune cell-mediated anti-tumor activity
- Greater in vitro ADCC and NK cell activation
Fcγ=Fc gamma.
References:
1. MARGENZA Prescribing Information. MacroGenics, Inc.; 2023.
2. Musolino A, Gradishar WJ, Rugo HS, et al. Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy. J Immunother Cancer. Published online January 6, 2022. doi:10.1136/jitc-2021-003171
3. Nordstrom JL, Gorlatov S, Zhang W, et al. Anti-tumor activity and toxicokinetics analysis of MGAH22, an anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody with enhanced Fcγ receptor binding properties. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R123. doi:10.1186/bcr3069.
4. Rugo HS, Im S, Cardoso F, et al. Efficacy of margetuximab vs trastuzumab in patients with pretreated ERBB2-positive advanced breast cancer: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. Published online January 22, 2021. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7932
The pivotal SOPHIA trial
See EfficacyBe in the know
Register for the latest information and updates about MARGENZA
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: LEFT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction: MARGENZA may lead to reductions in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Evaluate cardiac function prior to and during treatment. Discontinue MARGENZA treatment for a confirmed clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to MARGENZA during pregnancy can cause embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of the risk and need for effective contraception.
WARNINGS & PRECAUTIONS:
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
- Left ventricular cardiac dysfunction can occur with MARGENZA.
- In SOPHIA, left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 1.9% of patients treated with MARGENZA.
- MARGENZA has not been studied in patients with a pretreatment LVEF value of <50%, a prior history of myocardial infarction or unstable angina within 6 months, or congestive heart failure NYHA class II-IV.
- Withhold MARGENZA for ≥16% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values or LVEF below institutional limits of normal (or 50% if no limits available) and ≥10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values.
- Permanently discontinue MARGENZA if LVEF decline persists greater than 8 weeks, or dosing is interrupted more than 3 times due to LVEF decline.
- Evaluate cardiac function within 4 weeks prior to and every 3 months during and upon completion of treatment. Conduct thorough cardiac assessment, including history, physical examination, and determination of LVEF by echocardiogram or MUGA scan.
- Monitor cardiac function every 4 weeks if MARGENZA is withheld for significant left ventricular cardiac dysfunction.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, MARGENZA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Post-marketing studies of other HER2 directed antibodies during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death.
- Verify pregnancy status of women of reproductive potential prior to initiation of MARGENZA.
- Advise pregnant women and women of reproductive potential that exposure to MARGENZA during pregnancy or within 4 months prior to conception can result in fetal harm.
- Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months following the last dose of MARGENZA.
Infusion-Related Reactions (IRRs)
- MARGENZA can cause IRRs. Symptoms may include fever, chills, arthralgia, cough, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headache, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypotension, pruritus, rash, urticaria, and dyspnea.
- In SOPHIA, IRRs were reported by 13% of patients on MARGENZA plus chemotherapy. Most of the IRRs occur during Cycle 1. Grade 3 IRRs were reported in 1.5% of MARGENZA-treated patients.
- Monitor patients during and after MARGENZA infusion. Have medications and emergency equipment to treat IRRs available for immediate use.
- In patients experiencing mild or moderate IRRs, decrease rate of infusion and consider premedications, including antihistamines, corticosteroids, and antipyretics. Monitor patients until symptoms completely resolve.
- Interrupt MARGENZA infusion in patients experiencing dyspnea or clinically significant hypotension and intervene with supportive medical therapy as needed. Permanently discontinue MARGENZA in all patients with severe or life-threatening IRRs.
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse drug reactions (>10%) with MARGENZA in combination with chemotherapy are fatigue/asthenia (57%), nausea (33%), diarrhea (25%), vomiting (21%), constipation (19%), headache (19%), pyrexia (19%), alopecia (18%), abdominal pain (17%), peripheral neuropathy (16%), arthralgia/myalgia (14%), cough (14%), decreased appetite (14%), dyspnea (13%), infusion-related reactions (13%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (13%), and extremity pain (11%).
You may report side effects to the FDA at (800) FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch or to MacroGenics at (844)-MED-MGNX (844-633-6469).
INDICATION
MARGENZA is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist indicated, in combination with chemotherapy, for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who have received two or more prior anti-HER2 regimens, at least one of which was for metastatic disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: LEFT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction: MARGENZA may lead to reductions in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Evaluate cardiac function prior to and during treatment. Discontinue MARGENZA treatment for a confirmed clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to MARGENZA during pregnancy can cause embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of the risk and need for effective contraception.
WARNINGS & PRECAUTIONS:
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
- Left ventricular cardiac dysfunction can occur with MARGENZA.
- In SOPHIA, left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 1.9% of patients treated with MARGENZA.
- MARGENZA has not been studied in patients with a pretreatment LVEF value of <50%, a prior history of myocardial infarction or unstable angina within 6 months, or congestive heart failure NYHA class II-IV.
- Withhold MARGENZA for ≥16% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values or LVEF below institutional limits of normal (or 50% if no limits available) and ≥10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values.
- Permanently discontinue MARGENZA if LVEF decline persists greater than 8 weeks, or dosing is interrupted more than 3 times due to LVEF decline.
- Evaluate cardiac function within 4 weeks prior to and every 3 months during and upon completion of treatment. Conduct thorough cardiac assessment, including history, physical examination, and determination of LVEF by echocardiogram or MUGA scan.
- Monitor cardiac function every 4 weeks if MARGENZA is withheld for significant left ventricular cardiac dysfunction.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, MARGENZA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Post-marketing studies of other HER2 directed antibodies during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death.
- Verify pregnancy status of women of reproductive potential prior to initiation of MARGENZA.
- Advise pregnant women and women of reproductive potential that exposure to MARGENZA during pregnancy or within 4 months prior to conception can result in fetal harm.
- Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months following the last dose of MARGENZA.
Infusion-Related Reactions (IRRs)
- MARGENZA can cause IRRs. Symptoms may include fever, chills, arthralgia, cough, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headache, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypotension, pruritus, rash, urticaria, and dyspnea.
- In SOPHIA, IRRs were reported by 13% of patients on MARGENZA plus chemotherapy. Most of the IRRs occur during Cycle 1. Grade 3 IRRs were reported in 1.5% of MARGENZA-treated patients.
- Monitor patients during and after MARGENZA infusion. Have medications and emergency equipment to treat IRRs available for immediate use.
- In patients experiencing mild or moderate IRRs, decrease rate of infusion and consider premedications, including antihistamines, corticosteroids, and antipyretics. Monitor patients until symptoms completely resolve.
- Interrupt MARGENZA infusion in patients experiencing dyspnea or clinically significant hypotension and intervene with supportive medical therapy as needed. Permanently discontinue MARGENZA in all patients with severe or life-threatening IRRs.
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse drug reactions (>10%) with MARGENZA in combination with chemotherapy are fatigue/asthenia (57%), nausea (33%), diarrhea (25%), vomiting (21%), constipation (19%), headache (19%), pyrexia (19%), alopecia (18%), abdominal pain (17%), peripheral neuropathy (16%), arthralgia/myalgia (14%), cough (14%), decreased appetite (14%), dyspnea (13%), infusion-related reactions (13%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (13%), and extremity pain (11%).
You may report side effects to the FDA at (800) FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch or to MacroGenics at (844)-MED-MGNX (844-633-6469).
INDICATION
MARGENZA is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist indicated, in combination with chemotherapy, for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who have received two or more prior anti-HER2 regimens, at least one of which was for metastatic disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
